What is Damp proofing
During the construction of the building and after the completion of the building, water enters different parts of the building from different sources. It is called dampness.
This moisture also affects the beauty of the building. And also reduces the age of the building. Various measures are taken to protect the building from the ill effects of moisture, called Damp proofing.
Damp Proofing can be described in the following points;
- If faulty materials are used in building construction, there is a high risk of dampness.
- If second-grade bricks are used, or less cement is used in the plaster’s mortar will absorb moisture during the rains due to its higher water absorption capacity.
- Dampness becomes a problem even if the water supply or sanitary fittings are not installed properly during the construction of the building.
- To prevent moisture from entering the building, a horizontal damp proof course is provided on each wall at floor level.
- Exterior walls provide a vertical moisture barrier on the inside of the rooms.
- The horizontal DPC should never be below the floor. In addition, chemicals are used in DPC to prevent moisture.
Termite Treatment
Termites sometimes damage the building. Termites eat the wood Used in the building. Special techniques are adopted to protect the building from termites called Termite Treatment.
Sources of Dampness in Building
The following are different sources of moisture entering the building.
- Climatic Causes
- Structural Causes
Climatic Causes
Moisture enters the building through various natural sources. The details of these are given below.
- Rain causes water to reach different parts of the building, which takes the form of dampness.
- Groundwater levels usually rise significantly during rainy days. As a result, the foundation and other floors of the building are affected by damage to the building.
- Due to the increase in atmospheric pressure, the moisture in the air takes the form of water, which causes damage to the roof, floor, and walls. This condition occurs in severe winters.
- Rainwater collects under the building constructed in low-lying areas and damages the building.
- Due to the poor orientation of the building, some walls are more affected by rain because these walls are in front of rain and do not get much sun.
Structural Causes
Water used during building construction damages the building. In addition, the building is damaged due to poor construction; the details are given below.
- A lot of water is used during the construction of the building. Because of this, the walls of the building and other parts of the building stay wet for a long time. In this way, the salts in the building material dissolve in water and rise to the surface, causing damage to the building. If the wet walls and other parts of the building are plastered and painted before it dries, then the water in these parts will damage the building.
- Moisture also enters the building due to poor construction of the building. Poor construction includes non-standardization of DPC (Damp Proof Course), incorrect roof and wall joints, etc. In addition, water supply and sewerage pipes are not properly connected. Due to these reasons, moisture enters different parts of the building.
- Moisture also enters the building due to the use of defective material in the construction of the building. For example, if second-grade bricks are used, or less cement is used in concrete, the building will absorb moisture from the atmosphere. In addition, on rainy days, it will absorb more rainwater. It shortens the life of the building.
Bad Effects of Dampness
Dampness can cause the following damage to the building.
- iron used in building construction rusts.
- Moisture causes the plaster to crumble.
- The joint between the different layers of the floor expands.
- Moisture spoils the whitewash and painted surface.
- Salt accumulates on the surface of brick and stone masonry which causes the surface to deteriorate.
- Due to moisture, the wood used in the building starts to rot. In addition, the wood is, also affected by termites.
- Pipes and other equipment used for electrical installations and other facilities are damaged due to moisture.
- Moisture causes germs in the building, which has a detrimental effect on the health of the occupants of the building.
Prevention of Dampness
Various measures are taken to protect the building from the harmful effects of moisture. The details of these are given below.
- Damp Proof Course
- Use of Chemicals
- Surface Treatment
- Special Devices
Damp Proof Course
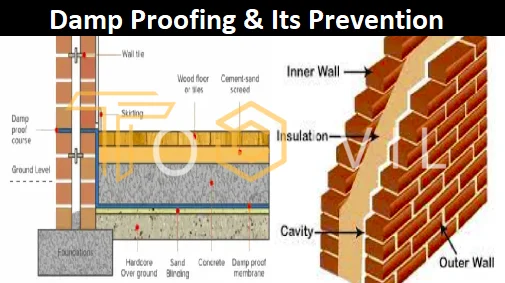
A waterproof layer is laid in the path of moisture to protect the building from moisture. This prevents moisture from entering the building. This layer is called D.P.C. (Damp Proof Course). This layer is usually laid in a horizontal position called horizontal D.P.C. Sometimes, this layer is laid vertically, called Vertical D.P.C. The D.P.C. layer usually consists of a layer of cement concrete in a 1: 2: 4 with a thickness of 3 to 5 cm (1.5 to 2 inches). The horizontal D.P.C. layer in the exterior walls of the building is placed 20 cm (9 inches) above the natural ground level (N.S.L.), which prevents rainwater from being absorbed into the building.

In interior walls, this layer of DPC is applied at floor level. This layer prevents moisture from entering the building from under the floor. The outer walls are lined with a layer of vertical DPC on the inside. The horizontal DPC joins the floor. Due to this vertical DPC, moisture gets through the filling material under the floor. Brass or aluminum is also used as a moisture barrier (DPC) in more important and valuable buildings
Surface Treatment
Paint is applied on the surface of that part of the building on which there is a possibility of rainwater or other water sources. Suppose this surface is located on the front side of f the building. If so, in addition to protectíon from moisture, beauty is also considered. For which beautiful paint is chosen. If this surface is located at the back of the building, a layer of bitumen is cut back to protect it from moisture.
Use of Chemicals
Materials used in building construction, such as concrete and mortar, are added chemicals that close the voids of concrete or mortar, due to which water cannot be absorbed in the surface. Calcium and magnesium compounds are commonly used for this purpose. Compounds of cooking oil, fat, and bitumen compounds are also used for waterproofing.
Their quantity should not exceed 2% of the quantity of cement. Iron Fillings are also used for this purpose. Waterproofing properties are also created in mortars or concrete prepared in a 5% soap solution.
Adding certain chemicals to mortars or concrete used for waterproofing also creates waterproofing properties. Chemicals used for waterproofing are being sold under various trade names, such as Impermo. These chemical compounds are used in the dry state by mixing 2% cement.
Special Devices
The following tricks can be adopted in building construction to avoid the harmful effects of moisture.
- The thickness of the exterior walls of the building should be kept more.
- Solid and non-absorbent materials should be used in the construction of exterior walls.
- More cement should be used for plastering the exterior walls.
- Excellent material used for drainage of rain and other used water from roofs and other parts of a building.
Damp Proofing Material
The following materials are used for damp proofing.
Bitumen Mastic
It is also called mastic asphalt. When mixed with sand, bitumen or asphalt becomes a non-absorbent mixture with a 2.5 cm to 5 cm thick layer that can only be laid in hot conditions, which cools to a
hard shape. This is a great way to absorb moisture. However, excellent care and caution are required when laying it so that the layer is perfectly smooth and can be spread evenly over the moisture paths; otherwise, it is not easy to remove from its place after cooling.
Bitumen Mats
6 mm thick bitumen mats are made, equal to the wall’s thickness. Its sheet is also available in the bazaar. It is laid the floor level above the wall. The sheet is well attached to the wall if it is to be used vertically as a moisture barrier so that no space remains.
Hot Layer of Bitumen
A DPC layer made of cement concrete is applied with two layers of bitumen on top of this layer. The average weight of bitumen should be 1.75 kg per square meter. It closes the pores of the concrete and gives it considerable resistance to moisture. It is mainly used in ordinary buildings.
Metal sheets
Lead. Copper or aluminum sheets are also used to retain moisture but are very expensive. These types of sheets should be spread over the entire thickness of the wall. The lead sheet should be Spread only with lime mortar. Otherwise, the chemical process on the lead starts with the cement mortar. Applying asphalt to lead and aluminum sheets gives better results. Copper sheets are best for retaining moisture and are long-lasting. These sheets should never be less than 3 mm in thickness.
Rich cement concrete
Where there is little moisture, a layer of prepared concrete (1:2:4) is laid from 1.2 cm to 4 cm thick, and hot bitumen is placed on it. Apply two layers for better results. This prevents the moisture from infiltrating
Rich cement mortar
A layer of at least 2 cm thick cement and sand mortar (1:3) acts as a vertical moisture barrier on the inner surface of the outer wall. On this layer, also two thin layers of hot bitumen should be applied for better results.
Requirements of Damp Proofing Material
Excellent damp proofing material should have the following properties.
- It does not absorb moisture.
- It should be durable.
- Do not break with impact load.
- It should not slip when its weight acts.
- It should easily cover the entire thickness of the wall.
- It should be easily available and affordable.
Principle of Use of Damp Proofing Material
- At least joints should be kept in the building.
- Damp proofing material covers the entire thickness of the wall
- Flexible material should be used on the joints of the walls.
- Damp proofing material should be overlapped on the corners of the walls and the joints between the walls.
- The layer of moisture-resistant material should be smooth and perfectly horizontal.
- Damp proofing material should not be used on doors and verandahs.
- If a sheet of lead is spread, it should be spread only with lime mortar.
- A damp proofing layer made of concrete or mortar should be thoroughly dried before coating the hot bitumen.
More Posts
FAQ’s
What are the advantages of damp proofing?
1. The first significant benefit of a damp proof course is that it will help us avoid any future health problems that the structure might experience.
2. The benefit of a damp-proof course is that it aids in preventing the musty, dank smell that untreated mold can leave behind around the property.
3. Eliminating the dampness with a damp proof course will lengthen the paint’s lifespan on the walls.
What is the most common cause of dampness?
Condensation is most common cause of dampness in homes, bedrooms, bathrooms, and kitchens. When warm moist air comes into contact with cold surfaces, water is deposited on the surface.
What are the 4 types of damp?
There are four types of dampness:
1. Damp Proof Course
2. Use of Chemicals
3. Surface Treatment
4. Special Devices
What are the causes of damp proofing?
Through damp proofing, buildings, and other structures are made so that water can’t get in. Depending on the location and construction of a structure, various factors can lead to dampness. Some of the most common causes of moisture are:
1. Condensation
2. Rising damp
3. Roof leaks
4. Plumbing leaks
5. Poor ventilation:
What is the colour of damp proof?
Dampproofing is not a color but prevents moisture from penetrating buildings or structures. The materials used for wet proofing can vary and may include coatings, membranes, or injections, but they typically do not have a distinct color. But dampness can often cause visible stains or discolorations on walls or other surfaces. Depending on the type of mold or mildew, these stains or discolorations can be yellow, brown, green, or black.
What is the best way to prevent rising damp?
To prevent rising dampness, the following steps can be taken:
Installing a DPC in the building is the best way to prevent rising dampness. A DPC is a barrier in a building’s walls or floors to stop water from rising. This can be done when the building is being built or afterward.
1. Maintain the existing DPC
2. Improve drainage
3. Ventilate the building
4. Use water-resistant materials
5. Repair any leaks