Introduction of Road Estimation
There are two types of complete estimation of roads.
- One of these types is the original work estimate, prepared to build a new road. Original work estimates include acquiring land for the road, Earthwork, Sub Base, Base, Surfacing, Road structures, and Installation of sign boards. It also provides demarcation and installation of cat eyes.
- The second type is called the repair estimate. Repair estimates include Resurfacing, Double Surfacing (D.S.T), Over Laying, and Raising. Road repairs usually begin four years after the road is built. The contractor is responsible for the damage to the road for one year after construction. After that, if a minor malfunction occurs, patchwork is done.
Structure of Road
When you cross the road from top to bottom, you can see different parts of the road.
Subgrade
This is the ground’s surface on which the road is built. Its surface is usually kept 60 cm (2 feet) above ground level so rainwater does not reach the road surface. If the road needs to be built in the cutting section, the subgrade is below ground level. The strength of the road depends mainly on that part.
Sub Base
This part is not an integral part of the road, but when the subgrade is weak, an additional layer of gravel or some other suitable material is provided to strengthen the road, called the sub-base.
Base
This is an integral part of the road. It bears the weight of the traffic moving on the road and safely transfers to the sub-base grade. The strength of the road depends on that part. This part of the road is usually made of solid gravel.
Surfacing
This is the road’s upper part, making the road surface smooth. It also makes the road surface impervious. This section determines the type of road. This section protects the lower part of the road.
Types of Roads
Roads are divided into two groups.
- Earthen Roacs
- Pucca Roads
Earthen Road
These roads are usually built in rural areas. The local soil of the area is used to build these roads. For a good road, the ratio of clay to sand should be 65:35. If the condition of the land is not good, then stabilization is done before building the road. In this process, the ratio of clay to sand is erected. Or cement., bitumen other chemicals are added to the soil. The roaá is then built from this soil.
Pucca Road
Pucca roads are good. These roads connect the country’s major cities and towns. There are two more types of paved roads.
Bituminous Road
Sub-base and bass layers are laid far in preparation for subgrade to make this type of road. A sub-base layer is made of bricks, gravel, or any suitable material, while the base layer is made of stone and gravel. A layer of priming coat is laid on top of the base layer. It consists of a mixture of bitumen and kerosene. Bitumen is spread over it as a tack coat, and the last layer is surfaced on top of it. That consists of Stone Metal and bitumen.
If the surface treatment consists of two layers, one is called Double Surface Treatment (DST); for better roads, three layers are laid, called Triple Surface Treatment (TST). Nowadays, most roads are constructed, for which the last layer is mixed with bitumen, aggregates, and sand in the hot state in the plant, and the top of the road is laid in the required thickness. Rooling is done the mixture contains 3 to 6% of bitumen. These roads are also called flexible roads
Concrete Road
Cement is used in the construction of these types of roads. These roads are long-lasting and do not require much attention to repair, but the structure of these roads is costly, so mostly, these roads are not built in Pakistan and India. These roads are constructed mainly in Saudia Arabia, UAE, and the USA(United-states). These roads are also called rigid roads.
Water Bounded Macadam Road
This paved road does not use any binding material such as bitumen and cement. After preparing the Subgrade for this road, the sub-base and the base layer are gravel. It is regularly compacted, and adequate water is used during compaction. Because this road is called Water Bound Macadam (W.B.M) Road, Bituminous Roads or Concrete Roads can be constructed on it.
Technical Terms of Roads
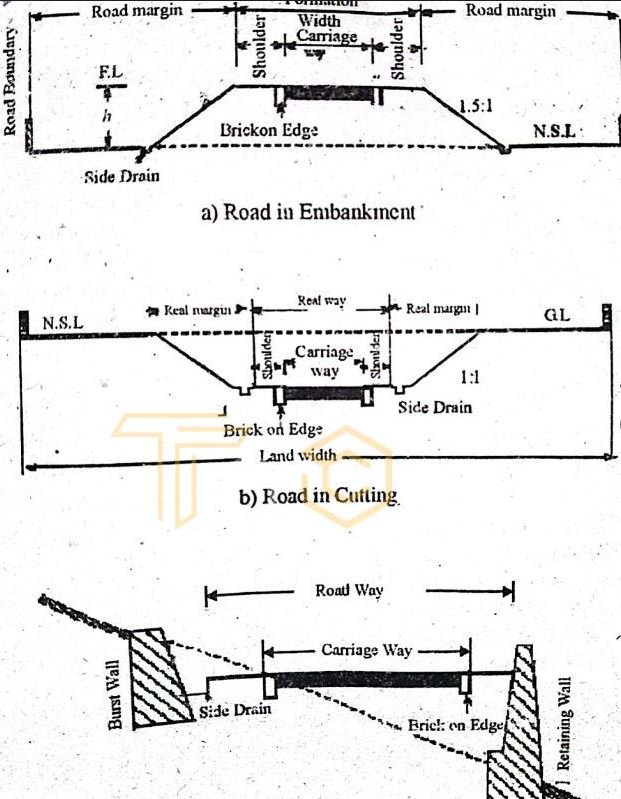
- Land Width: The total Width of a road owned by it is also called the Right of Way,
- Formation Width: The Width of the road at the prepared surface of the road is called formation width. It includes the paved part and the Width of the shoulder.
- Metaled Width: The paved part of the road on which high-speed traffic flows is called the Metalled Width. It is also called the carriageway.
- Shoulder: The surface left on the side of the paved road is called the shoulder. This part of the road is used to repair a vehicle malfunction or in case of another emergency. It is also called Berm.
- Side Slopes: Slopes are provided on the sides of the road from the level of formation to the ground level so that the road is safe. This slope is called the side slope.
- Gradient: The slope along the length of the road is called the gradient. If this gradient is towards the upside, it is called the Upward gradient; if it is the downside, it is called a downward gradient.
- Separator: Lines drawn to divide a road into two or more sections along its length are called separators. It is sometimes made of concrete or masonry. It is called a Grade Separator if it is used to separate different types of traffic.
- Footpath: A path parallel to the side of the road that is made for walking is called a footpath. Its Width is 1.3 meters (4 feet).
- Bicycle Track: The path made for cyclists towards the side of the road is called Bicycle Track. It is kept 2 meters 6 (feet) wide.
- Kerb Stone: An obstacle that separates a paved road and a sidewalk is called a curb. It is usually made of concrete blocks or stone.
- Camber: The slope facing the Width of the road is called camber. The purpose is to remove rainwater from the surface of the ròad.
- Crete Way: In low-lying roads, the road is sometimes paved just under the wheels of vehicles. Such roads are called the Crete Way.
- Urban Road: A road built in an urban area is called an urban road. In addition to the paved section of this road, sidewalks, and separators are also made.
- Country Road: A road built outside the urban population is called a country road. Footpaths are usually built on their sides.
- Service Road: A small road is made parallel to the main road, which is connected to the main road at some distance. The purpose of this road is to reach the surrounding buildings or market without disturbing the traffic on the main road
- Resurfacing: The prepared surface of the road is called surfacing. If this surface is damaged, it is called resurfacing if a layer of the same material is applied to repair it.
- Overlay: To repair a road, if the additional base material is put on top of the old road and three layers of surfacing are applied to it, it is called an overlay.
- Raising: If the old road is uprooted and filled with soil and the road is rebuilt on it, it is called raising.
- Arboriculture: Plantation along the roadside is called arboriculture.
Estimation of Roads
Some common steps to calculate the quantity of road:
- The length of the road is measured in meters or kilometers.
- The road’s width is measured in meters.
- Road Thickness must be measured in meters or centimeters.
- To determine the volume of the road in cubic meters, multiply the length, width, and consistency.
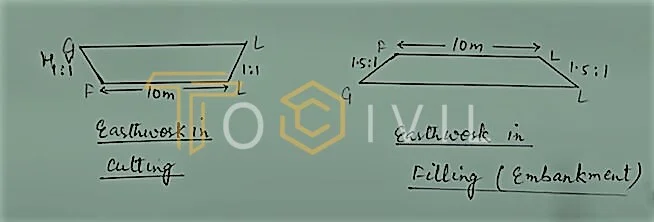
Earthwork Estimation in Road
Given data
Formation width = 10m, Side slope in cutting 1:1
Side slope in filling = 1.5 : 1
Falling Gradient = 1 into 200 from drainage 0 to 150 = 0.15
Falling gradient = 1 into 120 from drainage 150 to 300 = 0.25
Reduced Level(R.L) formation at chainage 0.00 to 102.50
| Chainage (m) | 0 | 30 | 60 | 90 | 120 | 150 | 180 | 210 | 240 | 270 | 300 |
| Ground Level (m) | 101.70 | 150.50 | 101.85 | 101.80 | 101.90 | 101.85 | 101.90 | 101.55 | 101.20 | 101 | 100.6 |
| Formation Level (m) | 102.50 | 102.35 | 102.20 | 102.05 | 101.90 | 101.75 | 101.50 | 101.20 | 101.0 | 101.75 | 100.5 |
| Cutting (m) | 3.50 | — | 0.10 | 0.40 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.10 | |||
| Filling (m) | 0.80 | 0.25 | 0.25 | — |
Rectangle divided into right triangles
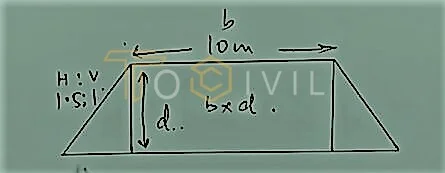
Area of Triangle = 1/2 x sd x d
Area of two Triangles = 1/2 x Sd2 x2
Area of Rectangle = Sd2 + b x d
When the Cross-section is found, then the quantity of road is fining by using the formula which is given below;
Quantity of Raod = Cross-section x Length(m)
| Chainage | Depth (m) | Area of two triangle sides sd2 | Area of two triangle sides sd2 | Total Area b.d+bd2 | Main Area (m) | Length (m) | Quantity | |
| 0 | 0.8 | 8 | 0.96 | 8.86 | — | 0 | Cutting | Filling |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.48 | 6 | 6.88 | |
| 30 | 3.15 | 31.5 | 9.92 | 41.42 | 20.71 | 24 | 497.04 | |
| 57 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20.71 | 27 | 559.91 | |
| 60 | 0.25 | 2.5 | 0.093 | 2.59 | 1.295 | 3 | 3.88 | |
| 90 | 0.25 | 2.5 | 0.093 | 2.59 | 2.59 | 30 | 77.7 | |
| 120 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.295 | 30 | 38.85 | |
| 150 | 0.1 | 1 | 0.01 | 1.01 | 0.505 | 30 | 15.15 | |
| 180 | 0.4 | 4 | 0.16 | 4.16 | 3.09 | 30 | 92.7 | |
| 210 | 0.3 | 3 | 0.09 | 3.09 | 3.62 | 30 | 108.75 | |
| 240 | 0.2 | 2 | 0.04 | 2.04 | 5.56 | 30 | 76.95 | |
| 270 | 0.25 | .2.5 | 0.062 | 5.56 | 2.3 | 30 | 69 | |
| 300 | 0.1 | 1 | 0.01 | 1.1 | 1.78 | 30 | 53.55 | |
Units of Measurements of Road Estimation
The following items are listed for estimating and payment for the road.
| Sr. No. | Particulars of item | Unit |
| 1 | Preparation of subgrade and setting camber and gradient etc. | Sft (sq.m) |
| 2 | PL of sub-base of approved quality and grade, including placing. Mixing spreading and compaction of sub-base material to the required depth. Camber. Rate to achieve specified dry density, including carriage of all material to the work site except gravel and aggregate. | Cft (cu.m) |
| 3 | Subsequent damage of gravel and crushed stone aggregate | Cft (cu.m) |
| 4 | P/L road edging | Rft (m) |
| 5 | We are providing and laying a base course of crushed stone aggregate of approved quality and grade and supplying and spreading stone screening, including placing, mixing, applying, and compaction of base course material to the required depth, camber, and angle to achieve specified dry density, including carriage of all materials to the site of work except gravel and aggregate. | Cft (cu.m) |
| Sr. No. | Particulars of item | Unit |
| 1 | Dismantling of dry brick masonry, road edging/selling | Cft (cu.m) |
| 2 | Dismantling and removing road pavement etc., including screening and stacking of by-products | Cft (cu.m) |
| 3 | Earthwork in ordinary soil specified for making embankment with lead and lift ic ploughing and mixing with blade grade of disc harrow or other suitable equipment and compaction by mechanical means at optimum moisture content dressing to designed section complete in all respect. | Cft (cu.m) |
| 4 | We are providing and laying the sub-base of the stone product of approved quality and grade ic placing mixing, spreading, and compaction of sub-base material i’c the setting of camber and grade. | Cft (cu.m) |
| 5 | Relaying of dismantled material (received after dismantling of road edging/pavement as Sub Base course of specified thickness complete in all respect (stone metal) completed to specified dry density i/c supplying mixing of fine material if required complete in all respect. | Cft (cu.m) |
More Posts
FAQ’s
What is the formula for calculating steel?
There are various formulas used in building construction that involve steel, depending on the specific application. Here are a few examples:
The formula is steel calculation: Weight (lbs) = length (in) x width (in) x Thickness (in) x density (lb/in^3). For example, let’s say you have a piece of 1/4″ thick steel plate that measures 7″ x 8″. To calculate its weight, use this formula: 7″ x 8″ x 0.25″ x 10.2 lb/in^3 = 142.6 lbs.
What are the two types of estimators?
There are two types of estimators.
Point estimator: A point estimator is a single value used to estimate an unknown population parameter.
Interval estimator: An interval estimator provides a range of values within which the population parameter is likely to fall, along with a level of confidence
What is a 2% slope?
A 2% slope means that the height changes by 2 units for every 100 units of horizontal distance moved. In other words, it’s a slope with a rise of 2 units for every 100 units of run.
For example, if a road has a 2% grade and is 1000 meters long, the change in elevation would be 20 meters (1000 * 0.02 = 20).
How do you calculate road gravel?
These are the main steps to figure out how much road gravel you need:
1. Measure the length and width of the road in meters.
2. Determine the desired thickness of the gravel layer in meters.
3. Convert the volume to cubic meters if necessary.
4. Find out how many kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m3) the gravel weighs.
5. Multiply the volume of gravel needed by the density of the material to get the 6 total weights of gravel needed: Weight = Volume x Density.
Which is the most accurate method of earthwork of road estimation?
The most accurate method of earthwork of road estimation is the Cross-Section method. This method involves taking measurements of the road surface at regular intervals along the road alignment, typically at intervals of 20-30 meters. These measurements are then used to create a series of cross-sections, which show the existing ground level, the proposed road formation level, and the required excavation or fill.
Differentiate between DST and SST?
Single Surface Treatment (SST): SST is a pavement surface treatment that involves applying a single layer of bituminous material (such as asphalt emulsion) onto the existing pavement surface.
Double Surface Treatment (DST): A pavement surface treatment involves applying two bituminous materials onto the existing pavement surface.