Introduction of Water Supply and Sewer Line
Water is used in homes, schools, colleges, shops, and other buildings, obtained from undèrground or surface water sources. It is cleaned and supplied to the place of use through designed pipes, and in the old day, open drains were constructed to safely takeoff this used water out of the population. Nowadays, most of the underground pipes are laid to carry this water. These pipes are called sewer pipes.
Water used indoors comes from bathrooms. Kitchens and latrines. When water from these places of use enters the pipe after use, traps are used at the entry location. These traps contain a certain amount of water at all times, which prevents dirty air from entering the house through the pipes. This system of water retention is called a water seal.
The water passes through the house drain and enters the sewer pipe left outside the street. But before entering the pipe left in the street, water passes through the gully trap. The sewer pipe left in the street is called the lateral pipe.
This water is removed from the population through the sub-main and central sewer. Sewer pipes are left in the road, and maintenance holes are constructed at the place of water entry in the sub-main. Maintenance holes are also constructed on the main sewer at a distance of 30 meters (100 feet) to 100 meters (300 feet) so that the inspection and cleaning of the sewer line can be done quickly.
Types of Pipes systems
- Separate pipe system
- Combined system
- Partially combined system
Separate pipe system
Separate pipes are sometimes laid to take stormwater out of the population, and different pipes are laid for domestic use. Such a system is called a separate pipe system.
Combined system
Sometimes the same sewer pipe drains domestic sewage and stormwater together. Such a system is called a combined system.
Partially combined system
Sometimes the sewerage system is designed so that a standard sewer pipe is laid in a populated area for both types of water. Still, stormwater is separated from the population. Such a system is called a partially combined system.
Nowadays, this system is much better. Each item of water supply and sanitation is measured Separately during detailed estimating. At the same time, the length of lines and the number of units are written by rough estimating.
Items of Work for Water Supply
| Sr. No. | Item of work | Measuring Units |
| 1 | Excavation according to nature of the soil, depth lead, and lift | m3 (1000 cft) |
| 2 | Concrete work According to grade of concrete anc. specifications: | m3 (100 cft) |
| 3 | Providing and fixing (P/F) pipeline according to kind of pipe and nominal diameter including jointing complete all respects. | m3 (100 cft) |
| 4 | Plaster or pointing work. According to specifications. | m2 (100 cft) |
| 5 | P/F urinal. according to type and size. | R.m. (Rft) |
| 6 | Providing and fixing (P/F) valves. According to type and size. | each no. |
| 7 | Providing and fixing (P/F) cocks. According to type anc. size. | each no. |
| 8 | P/F water closet (WC) according to type and size including flushing cistern. | each no. |
| 9 | P/F Bathtub. According to type and size | each no. |
| 10 | P/F wash hand basin (W.H.B) according to type and size. | each no. |
| 11 | P/F sink. According to type and size. | each no. |
| 12 | P/F fittings like towel rails. Soap dish, toilet pipe holder, etc. | each no. |
| 13 | P/F trap. according to type and size. | each no. |
| 14 | P/F Water tank. According to type and size. | each no. |
| 15 | P/F fittings like towel rails. Soap dish, toilet pipe holder etc. | each no. |
Estimation of Sewer Line
Préparation of Detailed Estimate of Sewer Line includes excavation, pipeline laying, jointing, and trench filling. The excavation also includes timbering to support the soil for large sewer lines. If the excavation is deep, then the work of dewatering the underground water is also involved. And it is not paid for separately, as well as the work of delivering the pipeline, laying it in the trench, joining, testing, and refilling. The pipe is laid on the ground in small lines in a ditch. Concrete is applied under the pipe joints in large lines, or gravel or concrete is laid in the entire line.
Estimates are made in the same way as the work is proposed.
Sewer Line Detail
How to Prepare Abstract Cost of Sewer Line? details are given below
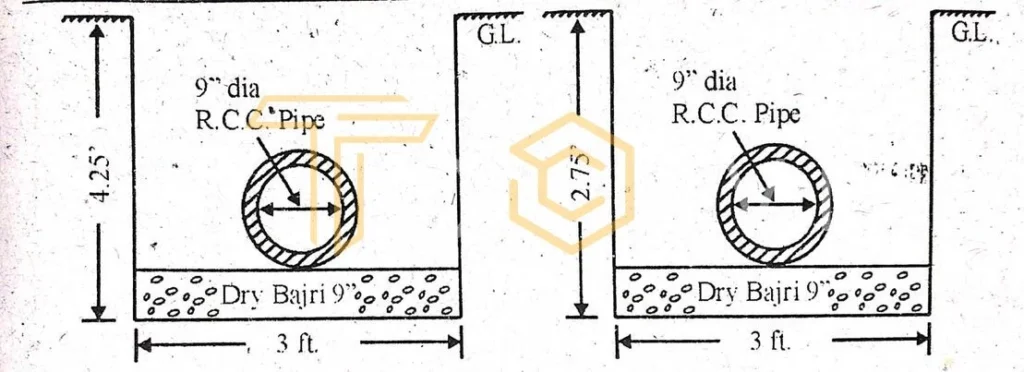
- Sewer Line = 300ft long
- Pipe Length = L = 6ft
- Breath = B = 3ft
The depth at the end point is 4.25 ft, and the slope is 200: 1 so,
Depth at First point = 4.25-300/200 = 2.75 ft
Abstract Quantities of Sewer Line
| Sr. No. | Description | No. | L | B | H | Q | Remarks |
| 1 | Excavation | 1 | 300 | 3.00 | 1.25+2.75/2 | 3150cft | |
| 2 | Providing and placing the crush in trenches | 1 | 300 | 3.00 | 0.75 | 675cft. | |
| 3 | Providing 9″ dia R.C.C. pipe, assuming 6 ft. Pipe length | 50 | – | – | – | 50Nos. | 300/6= 50 |
| 4 | Laying R.CC pipes and jointing | 300 | – | – | – | 300ft | |
| 5 | Refilling and raming the trench. Deduction for pipe Net quantity | 300 | As per item no.1 | π (0.75)2/4 | 3150cft 132.54 3017.46cft |
Abstract Cost of Sewer Line
| Sr. No. | Name of items | Quantity | Rate | Unit | Cost |
| 1 | Excavation | 3150 cft | 676.65 | 1000 cft | 2132.39 |
| 2 | Aggregate | 675 cft | 918.20 | 100 cft | 6197.85 |
| 3 | Providing 9″ dia Rcc pipes of length 6ft | 60 No | 348.90 | Per No | 17445 |
| 4 | Laying Rcc pipes | 300 ft | 10.10 | Rft | 3030 |
| 5 | Refilling | 3017.46 | 326.70 | 1000 cft | 985 |
Estimation of septic tank
In rural areas, septic tanks are constructed in factories without sewage treatment. They are built separately for each house, for a few houses or a small colony. The influent includes water from latrines and does not include kitchens, bathrooms, and rainwater. Inside this tank, bacteria dissolve human waste into water and gas.
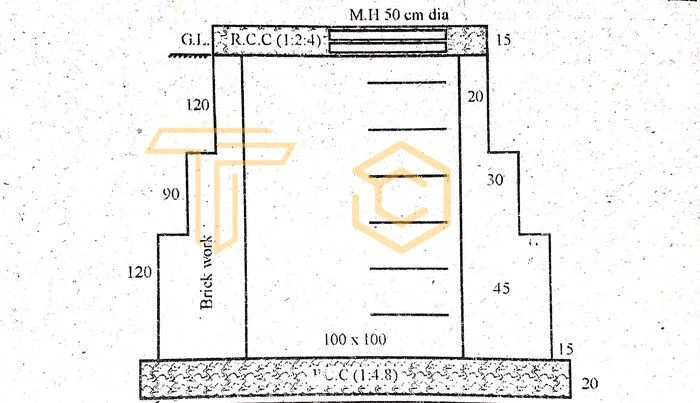
They leave a small amount of solid waste at the bottom of the tank, After six months or years, this waste is taken out and cleaned. While preparing the detailed estimate, the quantities of excavation work. Concrete work, brick masonry work. Baffle wall, slab and cover, etc., are known according to the drawings.
Septic Tank Estimation in Excel
| Sr. No. | Description | Nos | L | B | H | Q |
| 1 | Excavation | 1 | 3.8 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 11.62m³ |
| 2 | P.C.C (1.4:8) | |||||
| a) Base | 1 | 3.8 | 1.8 | 0.2 | 1.36m³ | |
| b) Slopping concrete | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0.06 | 0.18m³ | |
| Total | 1.54m³ | |||||
| 3 | Brick work in cement | |||||
| mortar (1:5) | ||||||
| a) Long walls (30cm) | 2 | 3.6 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 1.29m³ | |
| b) Short walls (30cm) | 2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.36m³ | |
| c) Long walls (20cm) | 2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 1.22m³ | |
| d) Short walls (20cm) | 2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 0.36m³ | |
| Total | 2.87m³ | |||||
| 4 | R.C.C (1:2:4) | |||||
| a) Slab | 1 | 3.4 | 1.4 | 0.1 | 0.476m³ | |
| b) Baffle wall | 1 | 1.2 | 0.04 | 0.5 | 0.024m³ | |
| Total | 0.500m³ | |||||
| Deduction | ||||||
| for Manhole cover | 1 | π (0.5) 2/4 | 0.1 | 0.02m³ | ||
| Net Quantity | 0.45m³ | |||||
| 5 | Plaster inside with cement | |||||
| mortar (1:3) | ||||||
| a) Long walls | 2 | 3 | – | 1.5 | 9.00m2 | |
| b) Short walls | 2 | 1 | – | 1.5 | 3.00m2 | |
| Total | 12.00m2 | |||||
| 6 | Manhole cover ci | 1 | – | – | – | 1 No |
| 50 cm dia | ||||||
| 7 | Iron steps @ 30 cm c/c | 4 | – | – | – | 4 Nos |
How does a septic tank work
A septic tank is a large underground concrete, fiberglass, or plastic container. It is usually buried near your house and is linked to your plumbing system by a series of pipes. The wastewater flows through the pipes and into the septic tank when you flush the toilet, shower, or do laundry.
The wastewater is separated into three layers once inside the septic tank. The lighter solids float to the top and form scum. The heaviest solids sink to the bottom and form sludge. The middle layer’s liquid effluent is then drained from the septic tank and into the drain field, where it is treated and absorbed into the soil.
Size of Septic tank
The size and other details of a septic tank for a different number of people are Different. The table below shows it.
| No. Users | Length (L) | Breadth (B) | Liquid Depth (D) | Liquid Capacity (LxBxD) | Liquid Capacity per user |
| 5 | 1.20m 4′ | 0.60m 2′ | 0.90m 3′ | 0.65 cu. m. (6501) 24 cu. ft. | 0.13 cu. m. (1307) 4.8 cu. ft. |
| 10 | 1.80m 6′ | 0.60m 2′ | 0.90m 3′ | 0.97 cu. m. (970/) 36 cu. ft. | 0.09 cu. m. (901) 3.15 cu. ft. |
| 20 | 2.50m 8′ | 0.75 m 2.5′ | 1.00m 3.5′ | -1.88 cu. m. (1880) 70 cu. ft. | 0.09 cu. m. (901) 3.5 cu. ft. |
| 30 | 2.80m 9′ | 0.75m 2.5′ | 1.20m 4′ | 2.50 cu. m. (25001) 90 cu. ft. | 0.084 cu. m.(84) 3 cu. ft. |
| 50 | 3.70m 12′ | 0.90m 3′ | 1.20m 4′ | 4.00 cu. m. (40001) 144 cu. ft. | 0.08 cu. m. (Sol) 2.88 cu. ft. |
| 100 | 4.30m 14′ | 1.20m 4′ | 1.40m 4.5′ | 7.22 cu. m. (72201) 252 cu. ft. | 0.072cu. m. (721) 2.52 cu. ft. |
| 200 | 5.50m 18′ | 1.80m 6′ | 1.40m 4.5′ | 13.86 cu. m. (138607) 486 cu. ft. | 0 069 cu. m. (691) 2.43 cu. ft. |
Septic tank cost
| Manhole. | Item. | Qty. | Rate. in INR. | Unit. | Cost in INR. |
| 1. | Excavation | 11.62 | 20/- | m3 | 232.4 |
| 2. | PCC | 1.54 | 150.15/- | m3 | 231.23 |
| 3. | Brick work in cement | 2.87 | 150.52/- | m3 | 432 |
| 4. | Plastering. | 327.5 | 15.10/- | m2 | 4,937.7 |
| 5. | R.C.C (1:2:4) | 0.45 | 100/- | m³ | 45 |
| 6. | The cost of a septic tank = | 1 | 1000/- | No | 1,000 |
| 7. | Vent pipe. | 1 | 300/- | No | 300 |
| 8. | Inlet & outlet pipe. | 2 | 150/- | No | 300 |
| Add 12% for contractors’ profit = | 20,317.4 | ||||
| The total cost of a septic tank = | 7,478.32 | ||||
| The total cost of septic tank = | 27,795.72 | ||||
Types of Septic Tank
There are different types of septic tanks depending on their needs, and conditions. Most of their types are listed below:
Conventional Septic Tank
A traditional septic tank is the most common type. It is made of concrete and has two sections. The wastewater flows into the first compartment, where the heavier solids settle to the bottom, and the lighter solids float to the top to form a scum layer. The liquid effluent is then drained into the second compartment, where further treatment takes place before it is discharged into the drain field.
Aerobic Septic Tank
An aerobic septic tank is similar to a conventional one but uses air to break down the waste. The tank has an air pump that pumps air to make it more oxygenated. This makes bacteria easier for metabolism of waste. An aerobic septic system is often used where the soil is unsuitable for a conventional septic system.
Cesspool
A cesspool is a type of septic system used when the soil is unsuitable for a drain field. A cesspool is a large, underground hole collecting and storing wastewater. Bacteria break down the waste, but there is no further treatment, and the effluent is typically discharged into a nearby water source.
Holding Tank
A holding tank is used when no suitable soil for a septic system exists. It’s a big subsurface tank that carries wastewater until it can be expelled and taken to a place where it can be cleaned. A holding tank is not a long-term solution and is typically only used in areas where other septic system options are unavailable.
Mound Septic System
A mound septic system is used in areas with high groundwater levels or poor soil conditions. The method involves building a raised bed of sand and gravel above the natural soil surface, which serves as a drain field. The septic tank effluent is pumped up to the mound and then trickles down through the sand and gravel, where it is further treated before being absorbed into the natural soil.
Advantages of Septic tank
- Cost-effective: A septic system is often more affordable than connecting to a public sewer system.
- Low maintenance: Septic systems typically require little maintenance if properly installed and maintained.
- Environmentally friendly: Properly designed and maintained septic systems are ecologically friendly, as they naturally treat wastewater and help to protect groundwater quality.
- Durability: Septic tanks are typically durable and can last decades if properly maintained.
Disadvantages of Septic tank
- Requires maintenance: While septic systems require less maintenance than other types of wastewater treatment systems, they still require regular maintenance to ensure they function correctly.
- Potential for backups: Septic tanks can back up and overflow if improperly maintained or overloaded.
- Potential health hazards: A septic system not correctly installed or maintained can pose a health hazard to nearby residents. Wastewater can contain harmful pathogens and pollutants that can cause health problems.
- Limited capacity: Septic tanks have a limited ability, so they may not be suitable for large households or properties with high water usage.
More Posts
FAQ’s
What is a concrete septic tank?
A concrete septic tank is made of concrete. It is a big, watertight container made to take in and treat wastewater from homes and buildings not connected to a city sewer system. The tank is divided into two compartments.
1. Baffle
2. Dividing Wall
The wastewater flows into the first compartment, where bacteria break down the solids that settle at the bottom.
how to check septic tank is full?
A few signs indicate your septic tank is full and needs to be pumped.
1. Slow draining fixtures
2. Unpleasant odors
3. Standing water
4. Backup in the plumbing
how much does it cost to pump a septic tank?
The price of pumping a septic tank relies on aspects such as the size of the tank, the location, and the service provider. On average, the cost range from $240 to $550. However, some companies may charge more or less than the given range. It’s essential to regularly pump your septic tank to prevent costly repairs or replacements down the line.
how to increase bacteria in septic tank naturally?
There are Different natural methods to increase the amount of bacteria in a septic tank, which can help to break down waste more effectively and keep the system running smoothly.
1. Use natural additives
2. Use less water
3. Avoid harsh chemicals
4. Add grass clippings or leaves
5. Use a septic tank treatment
Enlist the various names of sewer line?
There are a five names of sewer lines. which is given below
1. Horse drain sewer
2. Lateral sewral
3. Branch sewer
4. Trunk sewer
5. Main sewer
State the function of Trap in sewer line?
The purpose of the trap is to prevent the entry of dirty gases from sewer pipes into the house. When water flows through the trap, it fills up the U-bend. This makes a seal that keeps gases and smells from escaping through the drain. This keeps smells that could be dangerous or unpleasant from getting into the building and helps keep the air inside healthy.
Differentiate between Gully trap and Floor trap?
The gully trap is placed at the end of the house drain and before the lateral sewer so that the sewer’s dirty gases in the street do not enter the house. Floor traps are installed in bathrooms and kitchens at the drain entrance so that dirty gases from the drain cannot enter the rooms.