Many construction projects involve cutting or filling of earth. This work of cutting or filling the soil is called earthwork.
Introduction of Earthwork
This is more in the construction of buildings than in constructing roads, railway lines, and dams. Many earthworks are involved in making embankments along canals and the river. During earthwork, the soil is lifted from one place and thrown away in the other place.
- The work of soil where the soil is being lifted is called cutting, and the work where the soil is being dumped is called filling
- The lead is the horizontal distance from the ditch’s center to the filling’s center.
- The vertical distance between these centers is called the lift
- The higher the lead and lift, the higher the project cost. Although the quantity of earthwork will not change. Therefore, the amount of lead and lift should be as minimal as possible
- Earthwork is measured in cubic meters (cubic feet). These quantities are calculated at the čutting site.
If not possible, they are measured at the filling site and measured in the prepared form.
- Borrow Pit: The ditch from where the earth is excavated for earthwork is Called a borrow pit.
- Dead-man: In the borrow pit from where the earth is excavated, small columns of the earth are left to measure the depth of excavated soil, and those columns are called dead men.
- Lead & Lift: In earthwork, Soil is dug from one place, and this excavated Soil is stacked in another place. Thus, the horizontal distance between the Center of gravity of cutting and the Center of gravity where the Soil is being slacked is called a lead. The vertical distance between these centers is called a lift.
Value of Lead & Lift
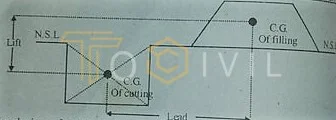
The design of roads, canals, or other projects ensures that the amount of lead and lift is minimal. Because as their quantity increases, the cost of the project increases. For road or canal construction, the amount of lead is usually 30 meters (100 feet), while the amount of lift is 1.5 meters (5 feet). In case of a large quantity of them, the contractor has to pay a higher rate. Sometimes the lift is converted to lead for payment. For which the following procedure is adopted.
| Value of Lift | Conversation Factor | Value of Lead |
| 1 | 8 | 8 |
| 2 | 8 | 16 |
| 3 | 8 | 24 |
| 4 | 8 | 32 |
| 5 | 10 | 50 |
| 6 | 10 | 60 |
| 7 | 10 | 70 |
| 8 | 10 | 80 |
| 9 | 11 | 99 |
| 10 | 12 | 120 |
| 24 | 26 | 624 |
| 25 | 27 | 675 |
| 26 | 27 | 702 |
| 27 | 27 | 729 |
Methods for Calculation of Earthwork
The land’s natural slope in the plains is shallow, and the area is smooth. The following methods are used to determine the amount of earthwork for road construction, embankment construction, and canal construction in the plains.
- Mean Depth Method
- Mean Area Method
- Prismoidal Method
- Graphical Method
Mean Depth Method
This method of determining the soil amount is also called the mid-section method. According to this method, identical slope and design sections of embankment or ditch are taken separately. Then the average depth value on both sides of each unit is found. These sections are usually 30 meters (100 feet) long.
The width of the earthen dam, the width of the bottom of the trench, and the side slope are determined by design. The depth varies on both sides of each section. The average value of these two depths is known, considered the depth in the middle of the section.
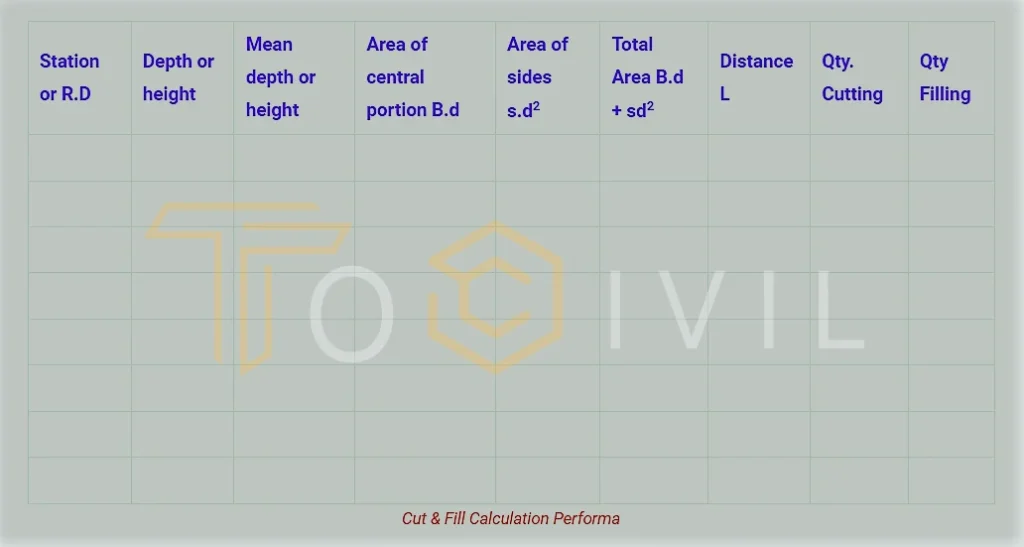
According to this method, the area is determined by finding the mean depth and multiplying this area by the length of the unit. The following formulas are used for
Mean Depth = d = d1+d2/2
Mean Area = A = B.d + sd2
Volume = v = (B.d + sd2) x L ; Where is L is Length of Section
If the embankment or trench length is too long, the following proforma is prepared according to this formula to determine the amount of earthwork in cutting and filling.
Mean Area Method
This method of determining the amount of earthwork is called the Trapezoidal formula. According to this method, the area of the cross-section is determined at a distance of 30 meters (100 feet) along the embankment or ditch.
Then the mean area is found from the areas of each of the two sections one after the other. This average area is then multiplied by the distance between the two sections to determine the amount of earthwork in cubic meters (cubic feet).

According to this method, the width of the top of the embankment or the width of the trench bed is known as the quantity of earthwork, denoted by “B.” In addition, the side slope is known, denoted by “S.”
The following formula is used to determine the amount of earthwork
Volume of earth = V = A1+A2/2 xL
A1 = B.d1+(Sd1)2
A2 = B.d2+(Sd2)2
Example
Given Data
Formation Width = B = 10m
Side Slope = s = 3 : 1
Depth at one end = 0.80m
Depth at other ends = 1.50m
Length of Section = L = 120m
Solution
Mean depth Method
Mean Depth = d = d1+d2/2
Mean Depth = 0.80+1.50/2
d = 1.153m
Quantity of Earthwork = v = (B.d + sd2) x L
Quantity = { 10 x 1.15 + 3(1.15)2 } x 120
V = 1856.10 cu.m
Mean Area Method
Area at one end = A1 = B.d1+(Sd1)2
Area = 10 x 0.80 + 3 x (0.80)2
Area = 9.92 sq.m
Area at other ends = A2 = B.d2+(Sd2)2
Area = 10 x 1.50 + 3 x (1.50)2
Area = 21.75 sq.m
Mean Area = A = A1+A2/2
A = (9.92+21.75)/2
A = 15.84 sq.m
Quantity of earthwork = A x L
V = 1900.80 cu.m
Prismoidal Method
This method is considered more accurate and better for determining the amount of earthwork. This method is used in places where quantities need to be determined more accurately. For this method, embankment or trench is divided into odd numbers. If their number is even, their quantities are known separately by dividing them into two parts, or the quantity of only one section is known separately. If there is only one section, the following formula determines the amount of earthwork.
V = L/6 (A1 + A2 + 4am)
Where V = Quantity of earth
L = Length of section
A1 = Area at one end of section
A2 = Area at other ends of section
Am = Area of mid section
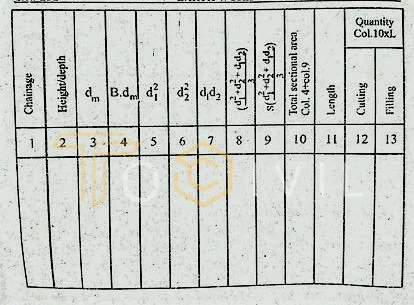
If the section consists of several sections and the length of each section is equal, then the following formula is used.
V = L/3 { First area + Last area + Σ even areas + 2 Σ odd areas }
The following table is also used to determine the amount of earthwork according to this formula for several sections.
Graphical Method
According to this method, a drawing is prepared according to an appropriate scale of embankment or trench. In this drawing, a long section and a cross-section are included. They show natural surface levels and formation levels.
After preparing this section according to the design, the areas for cutting and filling at each cross section for cutting or filling are known on the drawing. For this, the number of squares of graph paper is counted.
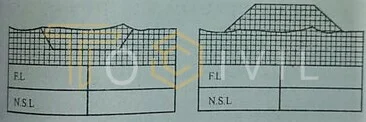
This number is multiplied by the value of one square to determine the value of the actual area to be cut or fill. When estimating the squares of a graph, when counting incomplete squares, half of them are included while the other half is ignored; this is called the give-and-take rule.
The quantity of earthwork is determined by multiplying the area between the two sections by multiplying the đistance between the two sections. In this field, this method is usually used to determine the quantity of earthwork
Calculation of Earthwork for Water Tank
The quantity of Earthwork for this tank is calculated by two methods.
- Mean Area Method
- Prismoidal Method
Calculation with Mean Area Method
Given Data
Length of the tank at Ground Level = 150ft
Breath of water tank at Ground Level = 100ft
Side Slope = 1:1
Solution
Length of the tank at the bottom = 150 – 2(S.d)
L = 150 – 2(1 x 15) = 120ft
Breath of the tank at the bottom = 100 – 2(s.d)
B = 100 – 2(1 x 15) = 70ft
The mean length of the tank = 150+120/2 ; = 135ft
The Mean Bearth of the tank = 100+70/2 ; = 85ft
Mean Area of tank = 135 x 85 ; = 11475sqft
The volume of Earthwork = V = Area x Depth
V = 11475 x 15 ; = 172125 cft
Calculation with Prismoidal Method
As per the given data which is shown above, Prismoidal Method will be like this:
The mean length of the tank = 150+120/2 ; = 135ft
The Mean Bearth of the tank = 100+70/2 ; = 85ft
Surface Area of tank = A1 = 150 x 100 ; = 15000 sqft
Bottom Area of tank = A2 = 120 x 70 ; = 8400 sqft
Mean Area of tank = Am = 135 x 85 ; = 11475 sqft
Prismoidal Formulas,
V = L/6 ( A1+A2+4Am)
V = 15/6 {15000+8400+(4×11475)}
V = 173250 cft
More Posts
FAQ’s
How do you calculate the earthwork slope?
To calculate the earthwork slope, measure the vertical rise and horizontal run between two points on the ground. The slope can be calculated by dividing the vertical height by the horizontal run. The result can be expressed as a percentage or a ratio. The formula for calculating the slope is:
Slope = Vertical Rise ÷ Horizontal Run
What is the formula for earthwork calculation?
The formula for earthwork calculation depends on the shape of the area being excavated. Here are some standard formulas for different shapes:
1. Rectangular or Square Shape: Volume = Length x Width x Depth
2. Trapezoidal Shape: Volume = (Top Width + Bottom Width) / 2 x Height x Length
3. Circular Shape: Volume = π x r² x Depth
It’s important to remember that these formulas only give an estimate of the volume of the earthwork. They don’t take into account any irregularities or changes in the excavation.
What is the difference between earthwork and excavation?
Earthwork is the process of shaping and leveling the ground surface for construction purposes, while excavation specifically refers to removing soil or rock from a site. Earthwork includes excavation as one of its components, but excavation is a specific type of earthwork.
Write the elements to calculate the Earthwork of roads in the plane area
There are four elements to calculate the earthwork of roads in a plane area.
1. Natural Surface Levels ( NSL )
2. Gradient
3. Formation Width
4. Side Slope
Write down the prismoidal formula to calculate earthwork for more than one section
The prismoidal formula is used to calculate the earthwork for more than one section which is given below;
V = L/3 { First area + Last area + Σ even areas + 2 Σ odd areas }
Define economical irrigation channel
Where the quantity of earthwork in excavation and filling is equal, this place is called the economical section, and the depth of excavation at this place is called the economic depth.
Define the intermediate point for earth work in a road section
When you go from filling to cutting or from cutting to filling, you come to a place where there is neither cutting nor filling; such a place is called an intermediate point.
